White light passing through a slit or from air into a prism generates a spectrum (rainbow). This is due to the fact that different component frequencies/wavelengths of the light refract (bend) by different amounts as they cross the boundary between the rarefied phase (air) and the condensed phase (glass or water). The phenomenon is known as the index of refraction. The technical origin for this effect is that the phase velocity (speed) of light in a condensed medium depends on its wavelength/frequency.
Remember the album cover for Dark Side of the Moon? CD, I meant CD case! You can easily find the image on the net. White light enters the prism from the left and a spectrum of light exits from the left. From top to bottom the colors are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet. Do you recall the mnemonic for the colors of the rainbow?
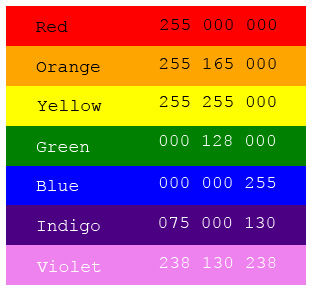
Spectrum with common synonyms and RGB decimal equivalents as defined in the HTML/CSS standard
Roy G. Biv : Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet, which is one more than on the Pink Floyd album cover. Why the difference? Well Isaac Newton made up this color series you see, and being a law-and-order sort of fellow he imagined that the light spectrum might be best understood by analogy to a musical (octave) scale. To make this work out he artificially added a seventh designation, indigo, between blue and violet. Of course visible light can be anywhere between red and violet. By the way, almost nobody can distinguish indigo in rainbows or in other diffraction experiments. Red light has the longest wavelength at 750-620 nm; orange ranges from 620-590 nm; yellow is narrow and between 590 nm and 570 nm; green is from 570-495 nm; blue is 495-450 nm; and violet is 450-380 nm. Longer wavelengths are known as infrared (more on this in a future entry) and shorter wavelengths are ultraviolet.
Notice that although the color spectrum represents a continuous variation from longer to shorter wavelengths, the decimal specification from the individual red, green, and blue channels is less than intuitive. Most of you already know that in this RGB system values can range from 0 through 255 inclusive, but why should the color red be defined as the full range of the R channel whereas the color green is only half of the maximal value? Is it at all obvious that violet should contain a half-maximal contribution from the green channel? In future entries we’ll return to the quantification and analysis of color, both as a diagnostic tool and as a method for maximizing the impact of the images. We’ll also consider another color space known as the Lab color space that provides a more intuitive connection between qualitative and quantitative interpretations of color.
By the way, the title of the song you are trying to recall is Brain Damage (hee hee!) . Now let’s try to keep the loonies on the path.
Tags: diffraction, Isaac Newton, Pink Floyd, rainbow, RGB, spectrum